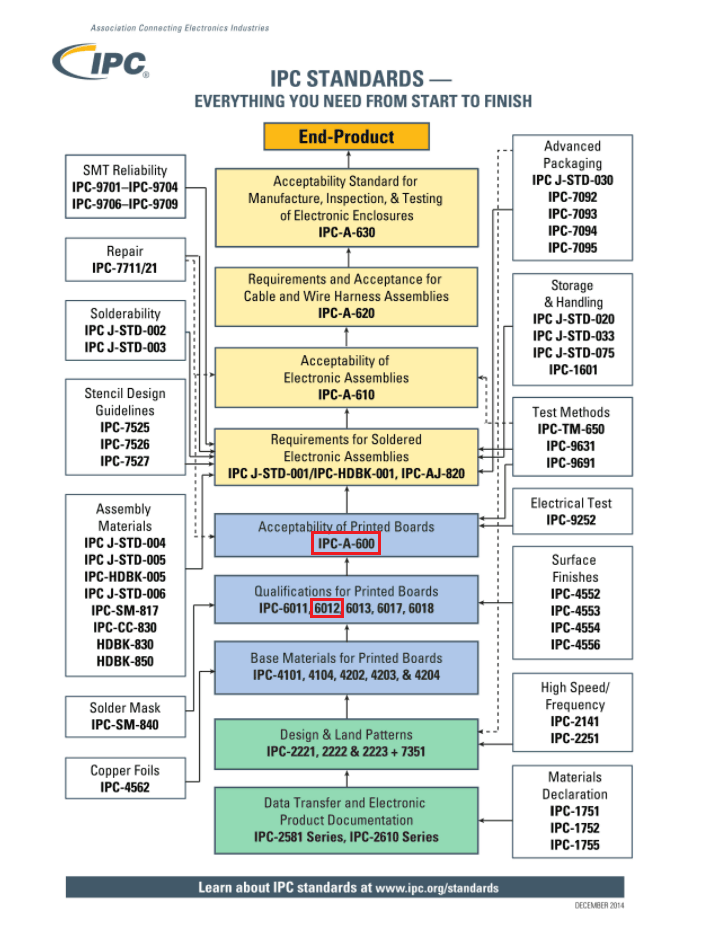
The IPC Standard Tree. – Image credit: IPC
The Association Connecting Electronics Industries – commonly known as IPC (Institute of Printed Circuits) – is an international trade association serving the printed circuit board electronics assembly industries. IPC is known globally for its standards that verify the quality of the manufactured PCBs PCB assemblies.
Manufacturers have to comply with many comprehensive inspection specifications that are in the IPC standard, designers have to be careful about IPC Class 2 Vs Class 3 different design rules, for instance.
IPC-6012 IPC-A-600 are two of the primary guiding documents, also called performance inspection documents. IPC-6012 is the specification IPC-A-600 is the visual representation of the IPC-6012 document. They both work hand in hand.
Recently, Leo Lambert, Vice President Technical Director of EPTAC, did a well-documented webinar about the topic. Thanks to his work, we will help you understand the differences between IPC-6012 IPC-A-600.
IPC-6012 is a specification which establishes defines the qualification performance requirements for the fabrication of rigid PCBs. The requirements apply to single-sided, multilayer boards, active/passive embedded circuity printed boards, HDI, metal core printed boards.
IPC-A-600 – also called IPC-600 – sets the level of acceptance criteria for each class of product. This document describes the target, acceptable, nonconforming conditions that are either externally internally observable on printed boards. It represents the visual interpretation of minimum requirements set forth in various printed board specifications such as IPC-6010 series.
The visual illustrations in the IPC-A-600 document portray specific criteria of the performance requirements of the applicable IPC-6010 series document.
Customers manufacturers can also agree on acceptance criteria that will replace the requirements of the appropriate IPC standard.
IPC-6012 is a performance specification. It defines default requirements what the specifications are required for each Class of PCBs.
Class 1 is assigned to general electric boards with a limited life a “simple” function, such as the ones you can find in remote controls.
Class 2 is for dedicated service electronic products, which means that you expect the board to have an extended life so you can place it in a television, a computer, an air conditioner.
Class 3 PCBs are tighter in tolerances as opposed to Class 1 Class 2 boards. They are high-reliability products used to achieve high performances in the military in medicine, for instance.
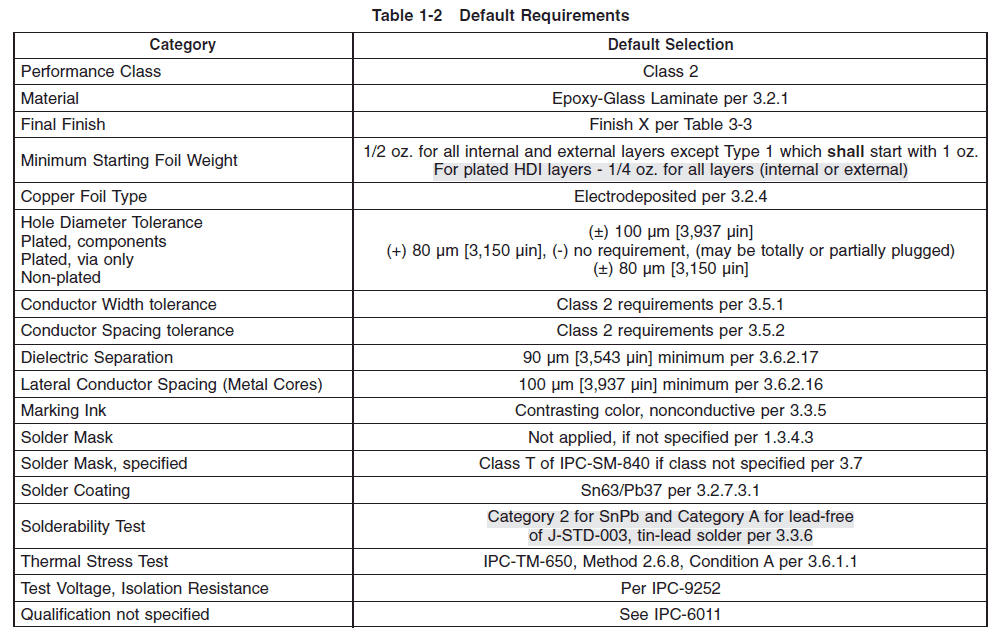
Class 2 is the default requirement. – Image credit: IPC
Here are some specifications for IPC-6012:
– visual
– solderability
– dimensional
– conductor width spacing
– conductor surfaces
– structural integrity
– cleanliness
When PCB designers are getting rigid boards fabricated, IPC-6012 is the spec they need to use. Designers use IPC-6012 to establish the requirements for the rigid boards they want. The document defines as well the requirements manufacturers have to meet during fabrication for three typical performance classes of boards – Class 1, Class 2, Class 3.
However, when manufacturers, are inspecting boards as they go to their facilities for assembly, they use IPC-A-600 for the upcoming inspection specifications.
Samhosoon is capable of certifying to IPC-6012, IPC-6013, IPC-6015, IPC-6018, as well as IPC-A-600.Please contact us for more!
Tel: 0086-0752-2690899
E-mail: sales001@samhosoon.com
Room 02/9F, Block 2, Dijing International Business center,
Yunshan West Road, Huicheng District, Huizhou, GuangDong, China
 |
| Mobile phone |
 |